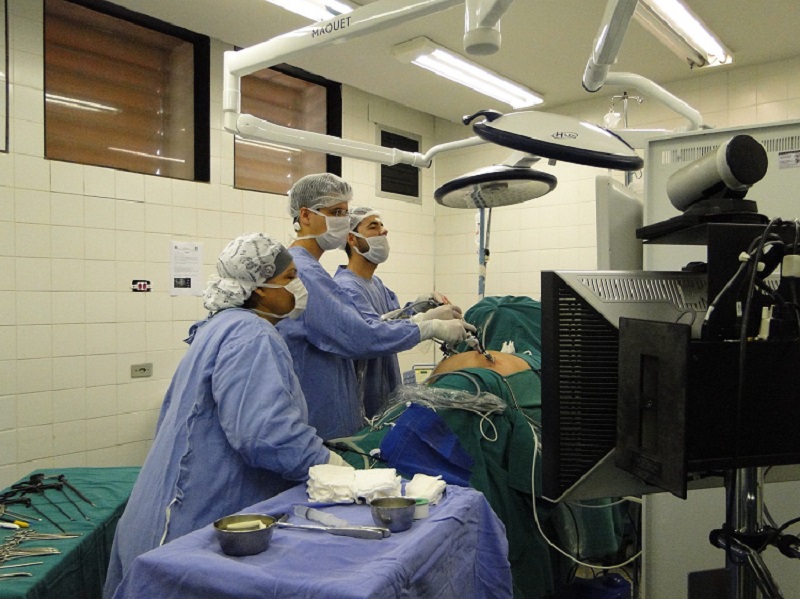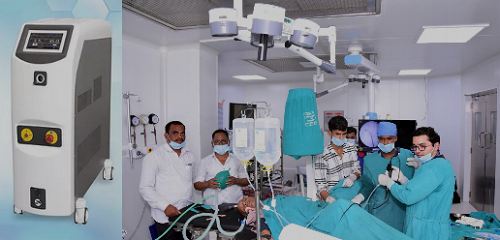
Laser lithotripsy involves the use of a laser to fragment stones into smaller, more manageable pieces that can be naturally passed out of the body. This procedure is often performed through a thin, flexible tube called a ureteroscope, which is inserted through the urinary tract to reach the stones.
Laser lithotripsy represents a significant advancement in stone removal procedures, offering a safer and less invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods. If you or someone you know is dealing with kidney stones or related conditions, consult with a healthcare professional to determine if laser lithotripsy is a suitable treatment option.
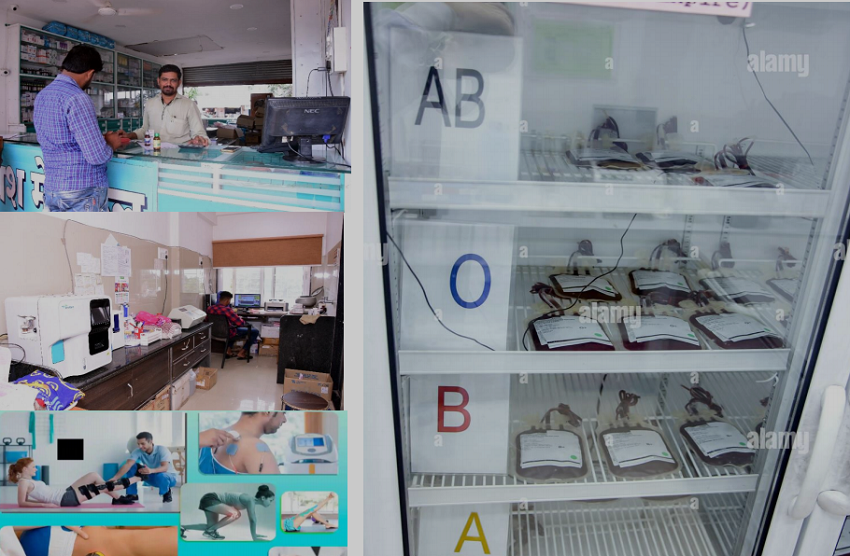
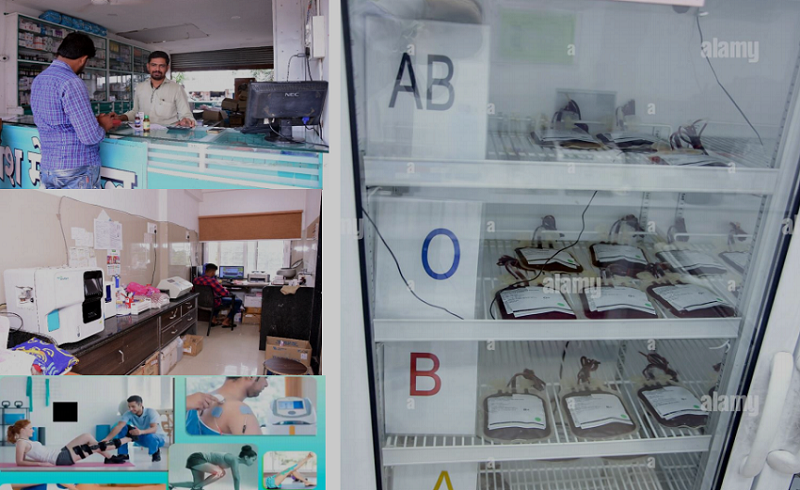
A pathology laboratory, commonly known as a path lab, is a facility where medical professionals analyze various biological samples to diagnose and monitor diseases. These labs play a crucial role in aiding physicians in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Blood storage units are facilities equipped to store donated blood and blood products. They play a vital role in ensuring a stable and safe blood supply for medical treatments, surgeries, and emergency situations.
A physiotherapy unit is a healthcare facility where trained physiotherapists provide rehabilitation services to individuals recovering from injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions. Physiotherapy focuses on restoring mobility, reducing pain, and improving overall physical well-being.

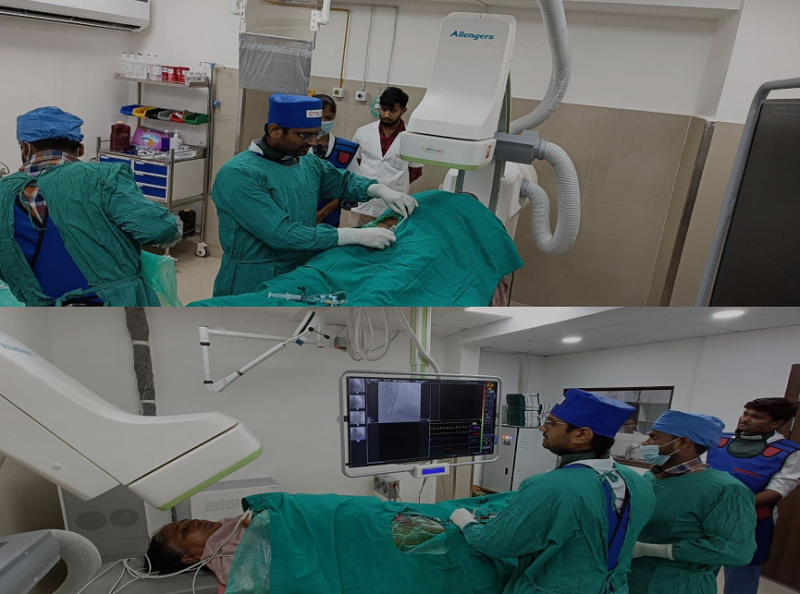
Angiography is a diagnostic procedure that involves the use of contrast dye and X-ray imaging to visualize blood vessels and assess their health and function. The procedure helps in identifying blockages, narrowing, or abnormalities in the blood vessels.
Angioplasty, also known as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), is an interventional procedure performed in the Cath Lab to treat narrowed or blocked blood vessels. It involves the use of a balloon catheter to widen the narrowed vessel and, in some cases, the placement of a stent to keep the vessel open.
The Cath Lab plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular conditions through advanced imaging and interventional procedures. It serves as a vital component in the management of heart and vascular diseases, contributing to improved patient outcomes and overall cardiac health.
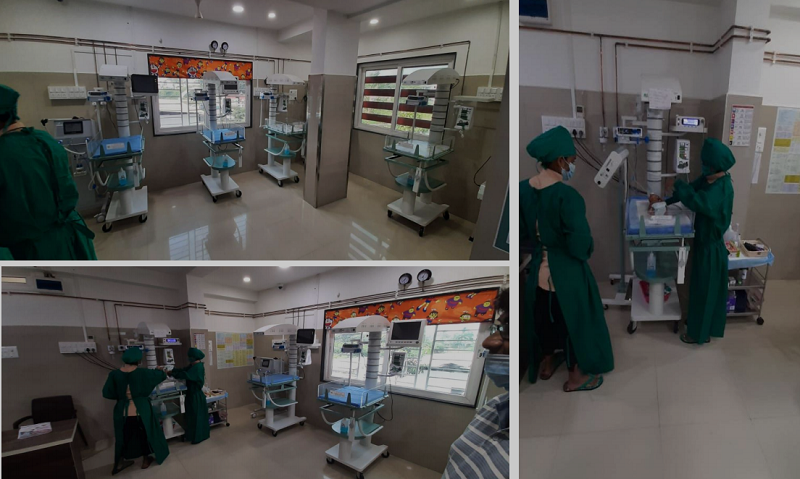
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) is a specialized medical facility designed to provide intensive care for newborn infants, especially those born prematurely or with medical complications. NICUs are equipped with advanced medical technology and a highly skilled healthcare team to monitor, diagnose, and treat newborns requiring specialized care.
NICUs play a crucial role in improving the survival rates and long-term outcomes for newborns facing medical challenges. The specialized care provided in NICUs helps support the growth and development of premature or critically ill infants, giving them a better chance at a healthy future.
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit is a vital component of modern healthcare, ensuring that newborns in critical condition receive the specialized care they need during the early days of life. The dedicated efforts of healthcare professionals in the NICU contribute significantly to the well-being and future health of these vulnerable infants.


A Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU) is a specialized medical facility within a hospital that provides intensive care for patients with acute and severe cardiac conditions. This unit is equipped with advanced medical technology and a specialized healthcare team to monitor, diagnose, and treat critical cardiac patients.
The Cardiac Intensive Care Unit is a critical component of cardiovascular care, providing specialized and immediate attention to patients with severe cardiac conditions. The combination of advanced medical technology, specialized healthcare professionals, and a comprehensive approach to patient care makes the CICU an essential unit in managing critical cardiac cases.
The neurology department is a branch of medicine that focuses on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders related to the nervous system. The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Neurologists are medical doctors who specialize in neurology and are trained to investigate, diagnose, and manage a wide range of neurological conditions.
Neurologists deal with a variety of neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, migraines, and various neuromuscular disorders.
Patients are usually referred to the neurology department by primary care physicians or other specialists when there are concerns about neurological symptoms or conditions.

Blood is typically stored in specialized facilities known as blood banks or blood centers. These facilities are responsible for collecting, testing, processing, and storing donated blood.
Blood and its components are stored at specific temperatures to prevent bacterial growth and maintain the integrity of the blood cells. Red blood cells are typically stored at temperatures between 1 to 6 degrees Celsius (33.8 to 42.8 degrees Fahrenheit).
Proper blood storage practices are essential for meeting the ongoing demand for blood transfusions in medical settings, such as surgeries, trauma care, cancer treatments, and other medical procedures.
Urology is a medical and surgical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders related to the male and female urinary tract and the male reproductive system.
Urologists often collaborate with other medical specialties, including oncologists, radiologists, and primary care physicians, to provide comprehensive care for patients.
If you are experiencing symptoms related to the urinary or reproductive systems, or if you have concerns about urological health, it is advisable to consult with a urologist. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a tailored treatment plan to address your specific condition.